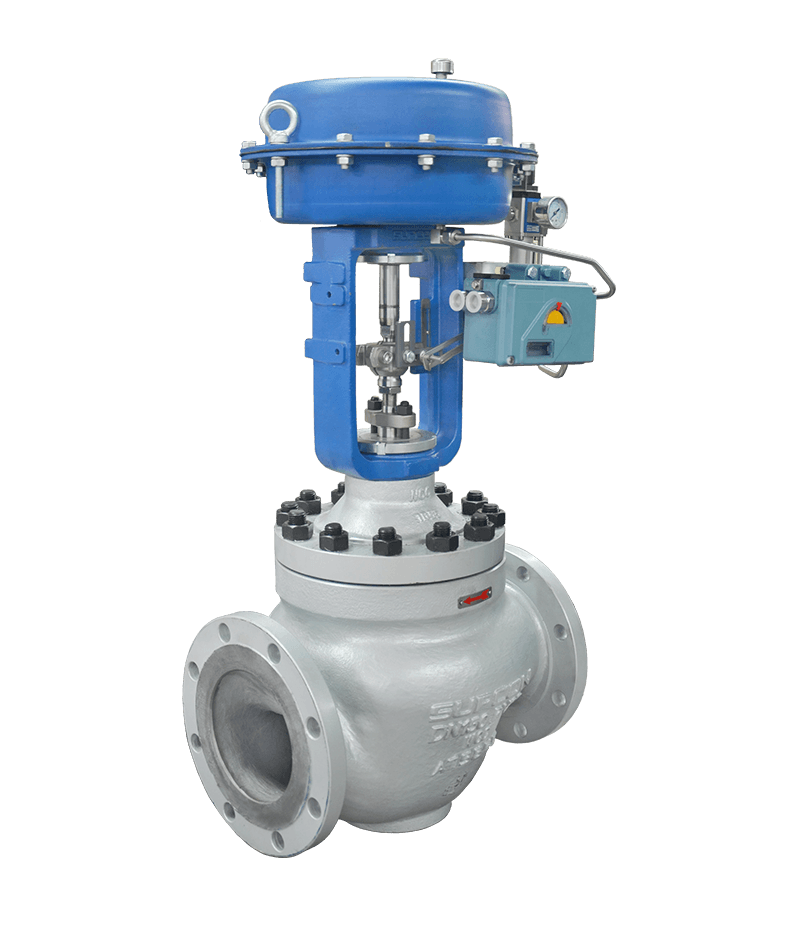
cage valve
Cage guided control valves offer stability in high pressure drop applications and reduce noise and vibration.

Cage guided control valves offer stability in high pressure drop applications and reduce noise and vibration.
The HSC and HCB series represent a sophisticated advancement in fluid regulation, designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern industrial process control. This cage valve architecture is engineered with an S-shaped flow passage that significantly reduces pressure loss while enhancing flow capacity by approximately thirty percent compared to conventional designs. The primary engineering focus is on providing a stable and balanced control solution for applications involving high pressure drops, where vibration and noise reduction are critical. Constructed with a heavy-duty body and a precision-engineered cage for plug guiding, this equipment complies with international standards such as PN16 to PN110 and ANSI Class 150 to 600.
As a high-performance flow management unit, this assembly is frequently utilized in complex thermal and chemical systems. The internal design is specifically capable of handling large flow rates and high differential pressures without compromising structural integrity. Whether configured with a standard bonnet for moderate temperatures or a radiator-style bonnet for extreme thermal service reaching up to 566 degrees Celsius, this regulation solution provides a robust barrier that maintains system reliability over a long operational lifespan.
The operational principle of this industrial assembly centers on a linear movement mechanism where the plug is guided along the entire stroke by a fixed internal cage. By physically separating the guiding function from the seat area, the device minimizes the risk of plug oscillation and ensures precise modulation even under turbulent conditions.
The core operational stages include:
To meet the demands of various chemical and thermal environments, these units are produced in several metallurgical configurations:
Carbon Steel (WCB, LCC) Series: These are the standard choices for non-corrosive service in refineries and power plants. They provide excellent structural durability and are suitable for temperatures from -29 to 425 degrees Celsius.
Stainless Steel (CF8, CF8M, CF3, CF3M) Series: Specifically designed for corrosive media, these models provide superior resistance to acid-base reactions and oxidation. They are essential for specialized chemical processing and the pharmaceutical sector.
High-Temperature Alloy (WC6, WC9) Series: For steam and high-temperature gas applications, these alloys maintain their mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, preventing deformation and ensuring long-term seat tightness.
Pneumatic Diaphragm Systems: Equipped with multi-spring actuators, these provide a rapid and fail-safe response, making them the preferred choice for automated plant control loops.
Electric Actuator Systems: Utilizing high-torque electronic units, these allow for precise digital control and feedback within a central control room, ideal for installations where compressed air is not available.
The integration of a cage-guided system provides several technical benefits that enhance the operational lifespan and safety of industrial infrastructure.
Enhanced Stability: The cage provides a large guiding surface that supports the plug throughout its travel, effectively eliminating the lateral vibrations often found in top-guided or bottom-guided valves.
Noise and Cavitation Control: By utilizing specialized cage hole patterns, the unit can effectively dissipate energy and reduce the noise levels generated by high-velocity gas or steam flows.
High Pressure Drop Capability: The balanced plug design in the HCB series allows the unit to handle much higher differential pressures than single-seated designs without requiring oversized actuators.
| Component | Example Materials | Performance Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Main Body | WCB, CF8, CF8M, WC9 | Robust design with S-streamlined flow path |
| Cage | 304SS, 316SS, Hardened Steel | Precise guiding and flow characteristic control |
| Balanced Plug | 304SS, 316SS, Stellite faced | Reduced actuator force and high stability |
| Seat Ring | 316SS, Stellite | Durable sealing surface and erosion resistance |
| Stem Packing | PTFE, Graphite | High-integrity external seal under pressure |
The versatility and robust design of the cage valve make it a critical component across numerous specialized sectors:
Request a Quote